Powder Generation¶
Powder Simulation¶
The powder generation software runs simulation of powder deposition.
Then a knife moves along x axis at the specified height.
The parameters are set in the same JSON file that is used in simulation. This helps with the consistency of simulation sizes.
Input Configuration¶
To start a simulation with internally generated powder layer, prepare a JSON file for your simulation as usual, but include the powder generation setting. As usual, if the setting is not included, the default value is used.
First, look at the Sizes and PowderBedGenerator sections of the input JSON file.
Here is the example
"sizes": {
"FullXapprox": 0.010,
"FullYapprox": 0.010,
"FullZapprox": 0.005,
"substrate" : 0.00456
},
"PowderBedGenerator": {
"Type": "PowDEM",
"RandomSeed": 0,
"GroundSurface": "",
"PSDsizes":
[[0, 45e-6], [5, 50e-6], [30, 60e-6], [50,70e-6], [70,80e-6], [90,90e-6], [100,100e-6]],
"KnifeZposition": 0.00466
},
Here are the solver options.
Key |
Value Type |
Value |
|---|---|---|
|
string |
PowDEM |
The name of the powder generator software. |
||
|
integer |
0 |
To generate different configurations of powder with same parameters, change this number to any other number. |
||
|
float |
0.00466 |
The height of the powder spreading knife (m). |
||
|
string |
“” |
Leave empty for powder deposition on a flat surface, specified with the |
||
|
list of value pairs |
[[0, 45e-6], [5, 50e-6],…} |
The distribution of powder sizes is set in the form \([[p_1,d_1],[p_2,d_2], ...]\), where \(p_i\) is the volume fraction of powder particles which have diameter less than \(d_i\). The pairs should be listed in order of increasing diameter. |
||
Here are the geometry options.
Key |
Value Type |
Value |
|---|---|---|
|
float |
0.010 |
|
float |
0.010 |
|
float |
0.005 |
|
float |
0.00456 |
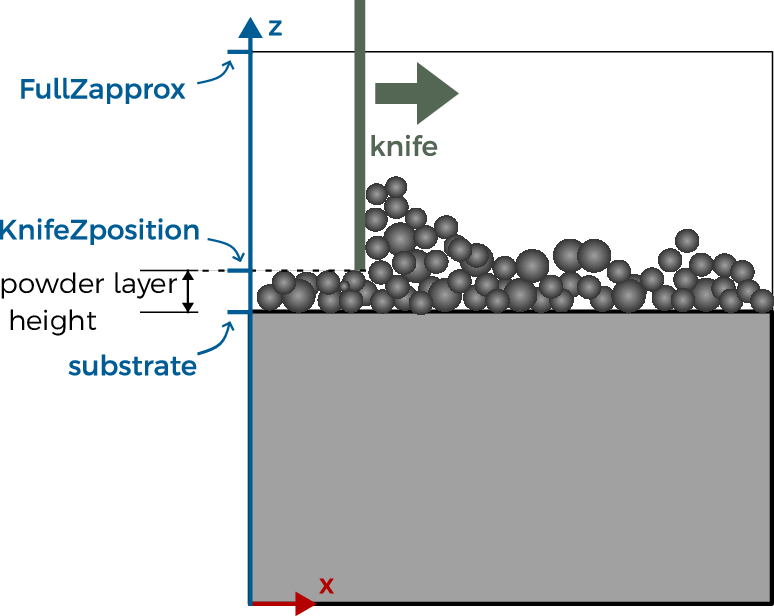
The FullXapprox\(\times\) FullYapprox (Here, 10 mm \(\times\) 10 mm) area is filled with powder. The height of the powder layer has to be (much) less than FullZapprox (m). The powder is set on the substrate, the height of the substrate is substrate (m).
These are the same fields that are used in the KiSSAM simulation.
The height of the powder layer is KnifeZposition-substrate (here, 0.1 mm).
\(0<\)
substrate\(<\)KnifeZposition\(<\)FullZapprox.
PowDEM run¶
Launch the powder deposition simulation with :
/share/bin/PowDEM [<default.json>] <input.json> [-n] [-v]
Or, if you have obtained the docker installation of KiSSAM,
docker run ... "PowDEM <input.json> [-n] [-v]"
If the fields which are required by the program are absent from the input.json file, they can be provided in the default file default.json
- -v¶
verbose output.
- -n¶
turn off interactrive graphics (recommended)


Output Files¶
spheres.datcontains the complete data of the generated powder geometry.
This is a text file and it contains four columns. For each sphere, its position (\(x\), \(y\), \(z\)) and radius (\(r\)) in μm are in one row.
27.4911 27.4917 27.4911 27.5
44.7133 79.1247 63.0167 37.5
87.07 32.4956 32.4953 32.5
166.9 34.6008 27.4979 27.5
128.672 75.4377 27.498 27.5
...
Before including the generated script in the KiSSAM simulation, spheres have to be rasterized with the rasterizeSpheres.x script.
powder_evolution.logcontains the detailed info of the particles dynamics and its relaxation to a steady-state solution.
It is a file in text format with several columns. Rows starting wit # are comments. Check this file during the simulation to check the integral values of the current powder geometry.
Example:
# Powder simulation convergence:
# t_sim Xmean Ymean Zmean Ymin Ymax Vmean V_Ymax V_0.99N maxV_traj maxV_insta Num_Particles
0 497.62 349.225 501.327 0 582.428 1 1 1 1 1 2098
...
1957.13 1234.56 494.681 41.2317 499.222 0 100.166 0.00786938 -0.0049597 0.0404546 0.0800193 0.147372 1084
The columns contain:
Column Key |
Description |
|---|---|
t_sim |
time in seconds |
X |
Knife position in \(x\) coordinate |
Xmean |
mean \(x\) position of particles |
Ymean |
mean \(y\) position of particles |
Zmean |
mean \(z\) position of particles |
Ymin |
minimal \(y\) coordinate (\(y\) is the vertical axis) |
Ymax |
maximal \(y\) coordinate (\(y\) is the vertical axis) |
Vmean |
mean velocity of particles |
V_Ymax |
velocity of max height change |
V_0.99N |
velocity of 99% fastest particle |
maxV_traj |
maximum trajectory velocity (\(\Delta x/\Delta t\) for a given time step Delta t) |
maxV_insta |
maximum instantaneous velocity |
Num_Particles |
number of spheres in the simulation |
powder_stats.logis a text log file which contains statistic information of the powder.
It might be useful in case of further powder analysis. This file contains the final thickness of the powder (the difference between the highest and lowest point of the powder by the vertical axis), the integral filling factor. It is followed by a table of three columns: particle size, distribution density by volume, distribution density by total amount, respectively. The file header is as follows:
# Final characteristics of the powder:
# Powder thickness (max) = 119.23 um, filling factor (mean) = 50.8124%. For more details please use spheres-analyze utility.
# PSD statistics:
# size_i(um) fi_volumetric fi_number
Use Powder in the Simulation¶
To use the prepared powder in the simulation, prepare the volumetric data from the spheres.dat file.
To do this, use the rasterizeSpheres.x script. For example,
/opt/KiSSAM/scripts/rasterizeSpheres.x 3 spheres.dat
Here, 3 is the mesh step in μm. The same mesh step should be used in the KiSSAM simulation in the NumericalParams.dr field (see JSON file description).
The file that is generated by the script should be specified as initial powder geometry is the simulation.
"Powder": {
"initSpheresVDBfile": "init_spheres.vdb"
}
Visualization controls¶
The visualization is interactive. The following keyboard and mouse actions control the run.
Space is to pause the simulation. Press Space again to resume the run.
Press w/e is to zoom in/out the picture.
Mouse buttons and actions
Press the middle mouse button (wheel) and move mouse to translate the picture.
Press the left mouse button and move the mouse to rotate the picture.